How a Payment Gateway Works: In the digital era, online payments are at the heart of eCommerce and digital business. But what exactly happens behind the scenes when someone buys something on your website? This is where payment gateways come in.
A payment gateway is the technology that captures and transfers payment data from the customer to the merchant and then to the bank, safely and efficiently.
Let’s explore how payment gateways work and why they’re essential for online business.
📌 What is a Payment Gateway?
A payment gateway is a secure bridge between your website or app and the financial institutions (like banks or card networks) that process payments.
Think of it as a digital version of a point-of-sale (POS) terminal, but for websites or mobile apps.
Popular examples include Razorpay, Paytm, Cashfree, CCAvenue, Stripe, and PayPal.

🔄 Step-by-Step: How a Payment Gateway Works
Here’s what happens when a customer makes a purchase:
✅ Step 1: Customer Places an Order
The buyer visits your website or app, adds items to the cart, and clicks “Pay Now.”
✅ Step 2: Redirect to Payment Gateway
Your system sends the user to a payment gatewy interface, where they select a payment method:
- Credit/Debit Card
- UPI
- Net Banking
- Wallets
- EMI or BNPL
✅ Step 3: Data Encryption & Tokenization
The gateway:
- Encrypts sensitive information (like card numbers or UPI IDs).
- Tokenizes data to protect customer details.
🔐 This ensures PCI-DSS compliance and keeps data secure.
✅ Step 4: Authorization Request
The encrypted payment data is sent to the acquiring bank (your payment processor), which then contacts:
- Card networks (Visa, MasterCard, RuPay, etc.)
- Or UPI/NPCI systems
- Then forwards it to the issuing bank (customer’s bank)
✅ Step 5: Bank Response
The issuing bank checks:
- Customer’s account balance
- Fraud patterns
- OTP verification or PIN
It then sends back a response:
- ✅ Approved (Payment successful)
- ❌ Declined (Insufficient funds, fraud alert, or incorrect details)
✅ Step 6: Transaction Complete
If approved:
- The payment gateway confirms the transaction in real-time.
- The customer is redirected to a success page.
✅ Step 7: Settlement
The money is first held by the payment gateway, and then:
- Transferred to the merchant’s bank account
- Usually within T+1 or T+2 working days
⚙️ Behind-the-Scenes Technology
| Term | What It Means |
|---|---|
| SSL Encryption | Secures payment data in transit |
| Tokenization | Replaces card numbers with secure tokens |
| PCI-DSS | Global security standard for handling card data |
| Webhooks | Auto-updates your app/website on payment status |
| API | Allows integration of the gateway into your site |
🧾 Real-Life Example
Let’s say Ramesh wants to buy a ₹999 Bluetooth speaker from your online store:
- He chooses to pay by credit card.
- Razorpay encrypts the card details.
- Data is sent to the bank, which authorizes it.
- Payment is approved.
- You and Ramesh both get confirmation.
- In 2 days, ₹969.64 (after fees) lands in your bank account.
🎯 Why a Payment Gateway is Important
- ✅ Secure: Protects user data
- ✅ Fast: Instant approvals and updates
- ✅ Multiple Options: UPI, Cards, Wallets, EMI
- ✅ Automated: Reduces manual billing or errors
- ✅ Trackable: View all payments in one dashboard
🛠️ How to Choose a Payment Gateway
Look for:
- Easy integration (APIs, plugins)
- Affordable pricing
- Instant or fast settlements
- Support for subscriptions, refunds, chargebacks
- International support if needed
🧠 Conclusion
Payment gateways are the digital cash registers of the modern age. From encrypting data to confirming transactions and managing settlements, they make sure money moves safely and smoothly between your customer and your bank.
Whether you’re a freelancer, a startup, or a large business—understanding how a payment gateway works helps you build trust and increase sales.


 Watch
Watch
 CASUAL WEAR
CASUAL WEAR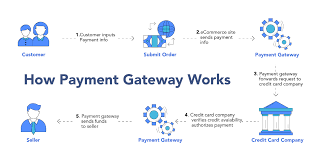

[…] Payment Gateway Recommendation For eCommerce stores in India, here’s a tailored recommendation for the best […]